In business, the right pricing strategies can mean the difference between success and failure. But with so many different options to choose from, it can be tough to know which one is right for your business.
That’s why we’ve put together this list of 17 pricing strategies that you need to know about. Whether you’re selling products, services, or subscriptions, there’s a method on this list that will help you get the most out of your prices. So read on, and find out which pricing strategy is right for you!
Pricing strategies and why they’re important
Understanding the complex dynamics of pricing is crucial for businesses looking to achieve success. Pricing strategies involve balancing customer and company interests in order to both meet customer needs and turn a profit.
It’s important to understand that price plays an integral role in the product life cycle: from initial launch, through uptake and use, to a steady decline.
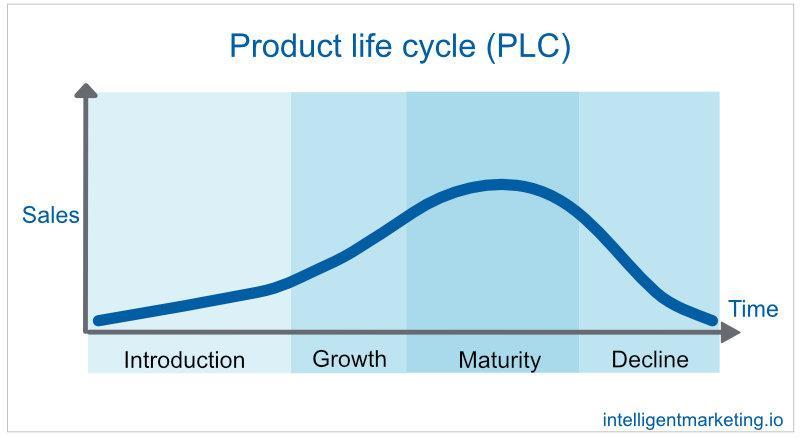
It also follows that changing the pricing point can help manage that decline and increase sales at different stages of the cycle.
New product pricing strategies
When launching a new product, companies must consider how best to price it. Marketers must evaluate whether:
- the new product is entirely novel in the existing market or in the new market,
- the product existing, but it’s a fresh introduction for the company in the existing market or in the market.
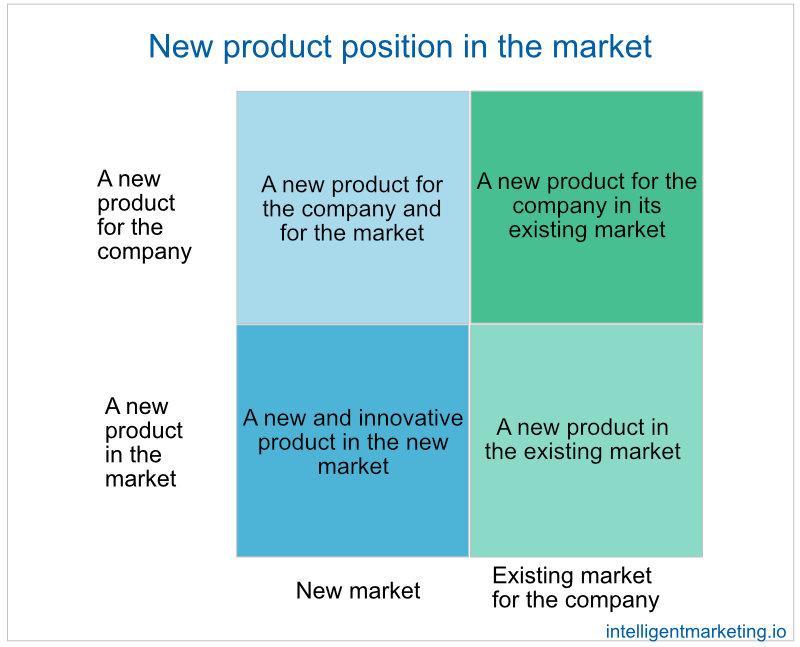
4 price-positioning strategies for new products
Prior to releasing their product, companies must strategically determine how to position it in comparison to other similar competitors’ products. With that in mind, marketers should consider which price-position strategy best suits their goals: premium strategy, good-value strategy, overcharging strategy, or economy strategy.
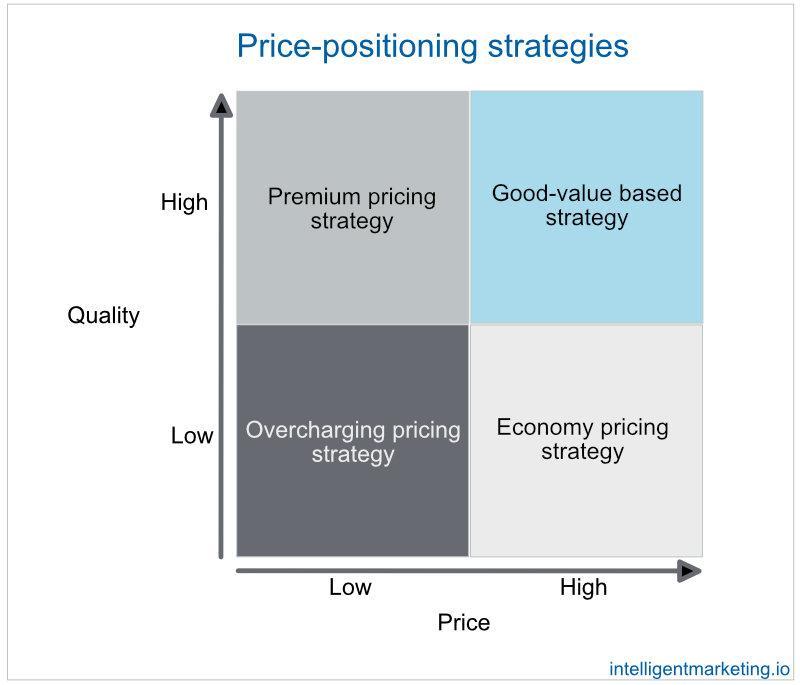
Premium pricing strategy (#1)
Premium pricing strategy involves setting a higher price for a product or service to reflect its high quality and status. This strategy is based on the idea that customers are willing to pay more for better quality products, as well as those with brand recognition and exclusive features.
With premium pricing, businesses can maximize their profits by charging more for their goods or services than competitors.
Additionally, it allows them to establish an image of luxury associated with their products—which in turn can attract new customers who are looking for something special.
Companies typically use this approach when launching a new product, especially if they have invested heavily in research and development costs.
Good-value pricing strategy (#2)
The good-value pricing strategy is designed to offer customers a product or service of high quality at an affordable price. This approach allows businesses to capture the attention of budget-conscious customers who are looking for the best value for their money.
Companies employ this strategy when launching new products, as it helps them gain market share by making their offerings more attractive than those of competitors in terms of cost and quality.
By offering high-quality goods or services at lower prices, companies can attract more potential customers while still maintaining a profit margin.
Additionally, this strategy can help increase sales volume and encourage customer loyalty over time.
Overcharging pricing strategy (#3)
An overcharging pricing strategy is a risky approach that involves setting high prices for products or services of low quality. This strategy relies on the assumption that customers are willing to pay more for goods and services simply because they cost more, regardless of their actual value.
Companies typically use this tactic when launching new products in order to cover research and development costs associated with them, as well as to make a quick profit.
However, it can be difficult to sustain such high prices without risking customer dissatisfaction and decreased sales volume due to the perception of low quality or poor value.
Therefore, businesses should carefully consider whether an overcharging pricing strategy is appropriate for their product before implementing it.
Economy pricing strategy (#4)
The economy pricing strategy is a pricing tactic that involves setting low prices for products or services of low quality. This approach allows businesses to draw in budget-conscious customers who are looking for the best value for their money.
Companies employ this strategy when launching new products, as it helps them gain market share by making their offerings more attractive than those of competitors in terms of cost and quality.
With economy pricing, businesses can minimize their costs while still maintaining a profit margin—allowing them to offer lower prices to potential customers without sacrificing profits.
However, this strategy can be risky if customers perceive the product’s quality as being too poor or lacking in features compared to similar offerings from competitors. Therefore, companies should carefully evaluate whether an economy pricing strategy is appropriate for their product before implementing it.
Market skimming pricing strategy (#5)
The market skimming pricing strategy is a tactic used by businesses to maximize profits from their new products. This approach involves setting high prices for goods or services of high quality in order to reflect its status and attract customers who are willing to pay more for better quality products with exclusive features.
With this strategy, businesses can capture the attention of those looking for something special while still maintaining a profit margin. Companies typically use this approach when launching a new product, especially if they have invested heavily in research and development costs.
Apple Inc. is an excellent example of a company that uses market skimming pricing strategy. Apple’s products are known for their high quality and advanced technology, which makes them attractive to customers willing to pay premium prices for the latest gadgets. This pricing strategy has allowed Apple to maximize profits from its new products while maintaining a large customer base.
Tesla is a company that has successfully implemented the market skimming pricing strategy. Tesla designs and manufactures electric vehicles (EVs) of superior quality and advanced technology. Tesla’s products feature impressive features such as all-electric powertrains, autopilot capabilities, over-the-air software updates, and more. These features enable Tesla EVs to command higher prices than competitors, allowing the company to maximize profits from its products.
Market penetration pricing strategy (#6)
The penetration pricing strategy is a tactic used by businesses to quickly gain market share. This approach involves setting low prices for products and services of high quality in order to attract customers away from competitors’ offerings.
Companies typically use this strategy when launching a new product or entering a new market. By offering lower prices than competitors, businesses can quickly gain market share and maximize their potential for long-term profits.
However, it is important to note that this approach requires companies to have tight control over their costs in order to ensure that they are still making a profit.
Amazon is a great example of a company that has successfully implemented the penetration pricing strategy. The company was able to quickly gain market share by offering its products at lower prices than competitors, allowing it to maximize long-term profits from its dominant position in the e-commerce industry.
Netflix is another example of a company that effectively used the penetration pricing strategy to quickly gain market share. The company offers a low-cost subscription service that allows customers to access its extensive library of movies and TV shows at a fraction of the cost of competitors. This allowed Netflix to quickly gain market share and become one of the leading streaming services in the world.
By using different new product pricing strategies, businesses can better position their new products in the market and maximize their profits. Companies should carefully evaluate which pricing strategy is best suited for their new product before implementing it. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, and only by understanding these can businesses make informed decisions about how to price their new products.
5 Product-mix pricing strategies
Product mix pricing strategies are an important part of a business’ pricing strategy. By offering customers different combinations of products at various prices, businesses can maximize their profits and increase customer satisfaction. This approach involves analyzing the individual price points of each product or service in a product mix and determining how those prices can be adjusted in order to maximize revenue.
Product line pricing strategy (#7)
Product line pricing strategy is a pricing approach used by businesses to maximize profits from their product offerings. It involves setting different prices for each product or service in a company’s product mix, based on the value it provides to customers and the cost of producing it. By offering different combinations of products at various prices, businesses can maximize their profits while providing customers with more options and increasing customer satisfaction. This approach allows companies to better position their products in the market and increase sales volume over time.
Samsung is an example of a company that uses a product line pricing strategy to appeal to different types of customers. The company offers a range of products including budget-class, mid-range, and premium models for their smartphones, tablets, and TVs. Each product has its own set of features and price points that are designed to meet the needs of different types of customers. This allows Samsung to capture more revenue from its product offerings and maximize its profits.
Optional-product pricing strategy (#8)
Optional-product pricing is a strategy used by businesses to increase their profits by selling optional or accessory products. This approach involves offering customers the option of purchasing additional products and services in addition to the core product they are buying.
By doing so, companies can increase their sales volume and maximize their profits from each customer transaction.
For example, if a customer is buying a new laptop, they may be offered an extended warranty or other accessories such as a carrying case or mouse at an extra cost. This allows businesses to capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added value for their purchases.
Apple is a company that effectively uses the optional product pricing strategy. Apple offers customers the option of purchasing accessories such as cases, chargers, and other add-ons along with their iPhones or Macbooks. By offering these extras at an additional cost, Apple can capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added convenience and value. Additionally, the company also offers extended warranty plans and subscription services such as Apple Music, iCloud storage, and Apple TV+ that customers can opt for at an extra cost. This helps Apple maximize its profits while providing customers with more options to choose from.
Captive-product pricing strategy (#9)
Captive-product pricing is a strategy used by businesses to increase their profits from the sale of related products. This approach involves setting different prices for each product or service that must be used together in order for customers to benefit from their purchase.
For example, ink cartridges and printers are often sold as a captive product set, with the printer being offered at a discounted rate if customers agree to buy the manufacturer’s ink cartridge along with it.
By offering these bundled packages at special prices, businesses can capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added value and convenience. Additionally, this approach allows companies to better position their products in the market and increase sales volume over time.
An example of a company that uses captive-product pricing is Microsoft. Microsoft offers customers the option of purchasing their Office software along with a laptop or desktop computer at a discounted rate. By doing so, customers get both products for one price and can use them together to maximize the benefits they receive from their purchase. Additionally, this approach allows Microsoft to capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added convenience and value.
By-product pricing strategy (#10)
Through the by-product pricing strategy, businesses can recognize revenue from low or no-value by-product outputs. This technique allows companies to monetize products they would have previously discarded.
For instance, plywood production yields chips as a by-product that can be sold to chipboard producers and lead to lower prices for the main product.
Product-bundle pricing strategy (#11)
Product-bundle pricing is a strategy used by businesses to increase their profits from the sale of related products. This approach involves offering customers multiple products at a discounted rate when they purchase them together. By doing so, companies can capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added value and convenience. Additionally, this approach allows companies to better position their products in the market and increase sales volume over time.
An example of a company that uses product-bundle pricing is Amazon. Amazon frequently offers customers discounts when they purchase multiple items together, such as books or electronics. By doing so, Amazon can capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added value and convenience. Additionally, this approach allows Amazon to better position its products in the market and increase sales volume over time.
Another example of a company that uses product-bundle pricing is Apple. Apple often offers customers discounts when they purchase multiple items together, such as iPhones or Macbooks with accessories such as cases and chargers. By doing so, Apple can capture more revenue from each sale while providing customers with added value and convenience. Additionally, this approach allows Apple to better position its products in the market and increase sales volume over time.
Thus, product-bundle pricing is an effective way for businesses to increase profit margins and capture more revenue from each sale. It can also be used to offer customers added value and convenience while positioning products more effectively in the market. Additionally, this strategy can help businesses increase sales volume over time.
6 Price-adjustment strategies
Price-adjustment strategies enable businesses to adapt their prices in response to changing market conditions and customer needs.
By using these strategies, businesses can ensure that they are providing customers with the right value for their products or services while also maximizing their profits.
Price-adjustment strategies come in many forms, including discounts, loyalty programs, promotional pricing and more.
These strategies allow businesses to adjust prices based on a variety of factors such as customer segmentation, seasonal trends, competitive pressures and other external influences.
Additionally, price-adjustment strategies can be used to incentivize certain types of behavior among customers or reward them for being loyal to the brand. As such, price-adjustment strategies are an important tool for any business looking to stay competitive in today’s ever-changing marketplace.
Discount and allowance pricing strategy (#12)
Discount and allowance pricing strategies are popular methods used by businesses to increase their profits while providing customers with added value.
This approach involves offering discounts or other incentives to incentivize certain types of behavior among customers, such as loyalty programs or promotional pricing.
Cash discount and volume discount
Cash discounts and volume discounts are two other popular types of discounts used by businesses. Cash discounts involve offering customers a reduced rate for making payments in cash. This type of pricing strategy can be effective in attracting customers, as it reduces the cost of goods and services for those who pay with cash.
Volume discounts, on the other hand, involve offering customers a reduced rate for purchasing higher quantities of a product or service. This allows businesses to capture more revenue from each sale while incentivizing customers to buy in bulk.
Quantity premium
It is a paid surcharge for buying high volumes of a product. It works because customers expect that the price per item in higher volume will be cheaper.
Seasonal discount
A Seasonal discount is a type of pricing strategy that involves offering customers discounts or other incentives during certain times of the year. This approach allows businesses to capture more revenue by leveraging seasonal trends, such as the holiday season or back-to-school sales.
For example, during the holiday season, many retailers offer discounts on gift items to attract customers. Similarly, businesses may incentivize customers with discounts during the back-to-school season to capture more sales from parents looking for school supplies for their children.
Overall, seasonal discount strategies can be effective in increasing profits and capturing more revenue from customers.
Allowances
This approach allows businesses to reduce the price of their products and services while also providing value to customers.
For example, if a customer returns an old phone or laptop, the business may offer them a discount on their next purchase.
Additionally, this strategy can help businesses increase sales volume over time as it encourages repeat purchases from loyal customers.
Segmented pricing strategy (#13)
Segmented pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering different prices to different customers based on their needs and preferences.
This approach allows businesses to customize their pricing strategies in order to capture more revenue from certain customer segments while providing value for others.
By segmenting their customers, businesses can better target specific groups with tailored discounts or promotions.
Additionally, this approach can be used to incentivize certain types of behavior among customers such as loyalty programs or promotional pricing. Segmented pricing is an effective way for businesses to maximize profits while also providing added value for their customers.
Customer-segment pricing
Customer-segment pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering different prices to different customers based on their needs and preferences.
This approach allows businesses to customize their pricing strategies in order to capture more revenue from certain customer segments while providing value for others.
An example of this would be when tickets for public transport vary according to the specific segment they are intended for, such as students or seniors.
Product-form pricing
Product-form pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering different prices for various versions of the same product.
This approach allows businesses to capture more revenue from customers who are willing to pay more for added features or services.
For example, a car manufacturer may offer different models of the same car at varying prices depending on their features and specifications. Customers can then choose which model they prefer based on their budget and needs.
Additionally, this strategy can be used by businesses to differentiate between products in order to capture more market share or attract new customers with lower prices. Product-form pricing is an effective way for businesses to maximize profits while also providing added value for their customers.
Location pricing
Location pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering different prices for products or services based on location.
This approach allows businesses to capture more revenue by leveraging local market conditions, such as demand and competition.
For example, a hotel may offer discounted rates in tourist destinations during peak season while charging higher rates in cities with less tourism activity.
Similarly, restaurants may adjust their prices according to the cost of ingredients or labor within a certain area.
Time pricing
Time pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering different prices for products or services based on the time they are purchased.
This approach allows businesses to capture more revenue by taking advantage of fluctuations in demand over time.
For example, an airline may offer discounted tickets during off-peak hours and higher rates during peak travel times.
Similarly, restaurants may adjust their menu prices according to the time of day or seasonality of certain dishes.
Time pricing can also be used by businesses to incentivize customers to purchase goods and services at specific times, such as discounts for early bird purchases or rewards for repeat customers who shop at certain times.
Psychological pricing strategy (#14)
Psychological pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering prices for products or services that are designed to influence customers’ purchasing decisions.
This approach allows businesses to maximize their profits by leveraging psychological factors such as perception, emotion, and behavior.
For example, businesses may offer discounts on certain items in order to create the illusion of value or use odd numbers such as $9.99 instead of $10 in order to make prices appear lower than they actually are.
By placing one budget-class product amidst premium goods, shoppers may falsely assume the budget item is of a higher quality.
Sometimes, premium products don’t always have a proportional correlation between their features and quality to the prices they are charged at; rather, those prices tend to be much higher than expected.
Promotional pricing strategy (#15)
Promotional pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves offering special discounts or incentives for products or services in order to attract customers. This approach allows businesses to capture more revenue by increasing customer demand and creating a sense of urgency.
For example, retailers may offer buy one get one free deals on certain items or provide discounts for customers who purchase large quantities.
Additionally, businesses may offer loyalty programs or coupons in order to reward repeat customers and encourage them to shop more often.
Promotional pricing can also be used by businesses to create a buzz around new products or services, as well as drive online traffic and generate leads.
Value-based pricing strategy (#16)
Value-based pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves setting prices for products or services based on the perceived value they provide to customers, not on cost. This approach allows businesses to capture more revenue by accurately reflecting the value of their goods and services. For example, businesses may charge higher rates for specialized products or services that require more expertise, resources, and time to deliver.
Geographical pricing strategy (#17)
Geographical pricing is a type of price-adjustment strategy that involves setting prices for products or services based on the geographical location of customers.
Marketers must determine whether to charge for delivery and the price point.
Conclusion
Pricing strategies are an essential part of any business and can have a major impact on the success or failure of your product. With so many pricing strategies available, it’s important to experiment with different options to find out which one works best for you. Additionally, keep an eye on what your competitors are doing in order to stay competitive. As long as you take the time to research all your options carefully, finding the right pricing strategy should be easier!
